Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
FOXO4-DRI 10 mg
FOXO4-DRI is a laboratory-designed retro-inverso peptide based on the FOXO4 protein, engineered to remain active for longer in the body and to disrupt the usual interaction between FOXO4 and p53, a key factor that often keeps damaged, senescent cells from being cleared. When this connection is blocked, those aged or malfunctioning cells are more likely to undergo programmed cell death, which can help remove them from tissues. Experimental work suggests that eliminating these so-called “zombie” cells may help restore more normal tissue performance, ease chronic inflammation, and support healthier organ function. In animal research, FOXO4-DRI has been associated with improved cellular renewal, increased vigor, and mitigation of certain biological markers of aging, while also influencing oxidative balance, the way the body responds to insulin, and the regulation of the cell cycle. As a result, it is being explored as a potential senolytic agent in studies focused on long-term health and regenerative therapies.
$340.00
All Products
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
Overview of FOXO4-DRI
FOXO4 D-Retro-Inverso is a modified version of the normal FOXO4 protein in which the usual L-amino acids are replaced with their D-forms and arranged to resist rapid breakdown. This alteration greatly slows enzymatic degradation in the body, so the peptide persists longer while still interacting with key signaling pathways and influencing gene activity. Functionally, FOXO4-DRI behaves as a selective disruptor of native FOXO4 activity inside cells.
A major area of interest for longevity research is how FOXO4-DRI affects senescent cells. In aging or heavily damaged cells, FOXO4 normally binds to the p53 protein and keeps it from fully triggering programmed cell death. FOXO4-DRI competes for p53, loosening FOXO4’s hold and allowing p53 to act on DNA and complete the apoptosis program. This effect appears to be biased toward senescent, non-functional cells, so the peptide helps remove “worn-out” cells while sparing healthier ones. Clearing these cells can improve tissue performance, reduce harmful signaling from senescent cells, and create space and resources for younger cells to repair and repopulate tissues, effectively improving biological youthfulness.
Retro-Inverso Peptides in General
Retro-inverso peptides are custom-built chains where the amino acid order is reversed and the building blocks are switched to D-amino acids so that the overall three-dimensional arrangement of side chains mimics the original natural peptide. This design usually makes them far more resistant to enzymatic breakdown, which means they remain active in biological systems for a longer time compared to standard L-peptides.
Using D-amino acids provides several advantages: the peptide backbone is less vulnerable to common proteases, the effective lifetime in circulation is extended, and bioavailability can be improved when the sequence is planned carefully. Designers can place D-amino acids in specific regions, in blocks, or alternating with L-amino acids to tune stability and biological activity. When the geometry is matched well, retro-inverso constructs can bind to the same targets as the original peptides while being considerably more robust.
Because they can faithfully imitate the surface features of natural peptide regions, retro-inverso molecules are widely used as peptidomimetics to probe protein–protein and protein–peptide interactions, or to stand in for natural epitopes in experimental systems. They are also attractive drug prototypes, since their enhanced stability and generally lower tendency to provoke immune reactions can make them more suitable for therapeutic development than many unmodified L-peptides.
FOXO4-DRI Peptide Structure
Sequence: H-D-Leu-D-Thr-D-Leu-D-Arg-D-Lys-D-Glu-D-Pro-D-Ala-D-Ser-D-Glu-D-Ile-D-Ala-D-Gln-D-Ser-D-Ile-D-Leu-D-Glu-D-Ala-D-Tyr-D-Ser-D-Gln-D-Asn-D-Gly-D-Trp-D-Ala-D-Asn-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Ser-D-Gly-D-Gly-D-Lys-D-Arg-D-Pro-D-Pro-D-Pro-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Gln-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Lys-D-Lys-D-Arg-D-Gly-OH
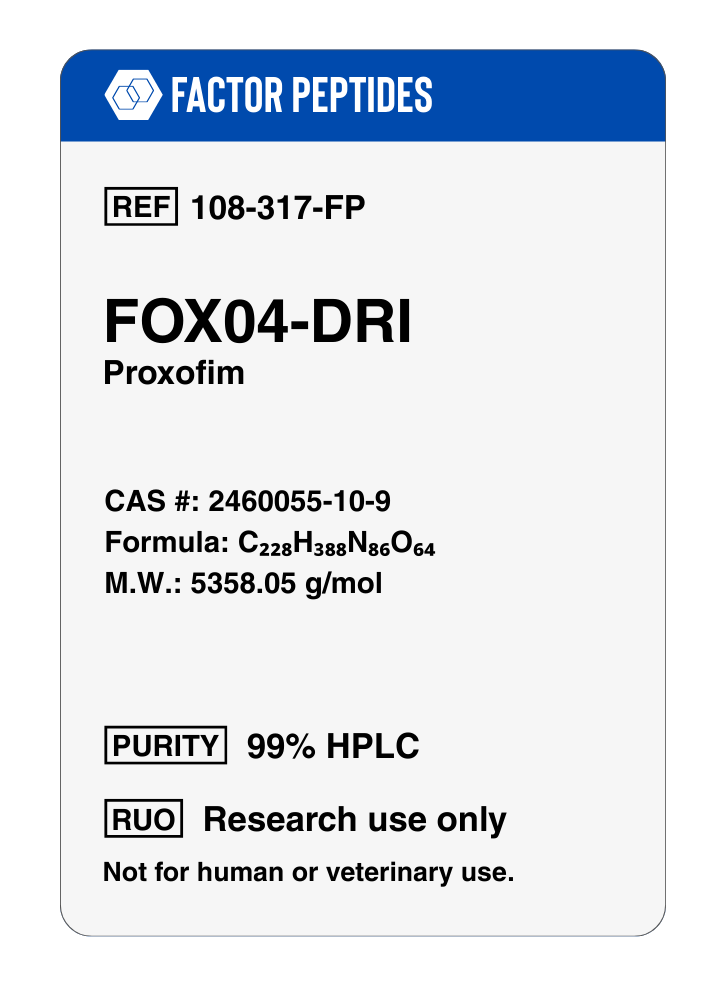
Molecular Formula: C228H388N86O64
Molecular Weight: 5358.05
Synonyms: Forkhead box protein O4, Proxofim, FOXO4a, AFX, AFX1, MLLT7
FOXO4-DRI, Aging, and Cellular Senescence
FOXO proteins are central regulators of stress resistance, metabolism, and lifespan control, but their exact role in aging is still being clarified. Work in small model organisms shows that FOXO activity is tightly linked to insulin-like signaling, oxidative stress responses, and broad gene expression programs that influence how long cells and tissues remain functional. In higher organisms, FOXO proteins also cooperate with p53 to control whether cells repair themselves, pause, or undergo apoptosis.
In senescent cells, native FOXO4 forms a complex with p53 that helps keep these cells alive despite being damaged and no longer dividing. FOXO4-DRI disrupts this protective arrangement, freeing p53 to fully engage the apoptotic machinery and selectively eliminate senescent cells. As these non-productive cells are removed, tissue balance improves, chronic low-grade inflammation is reduced, and younger cells have a better environment in which to maintain normal function. Animal studies have reported improvements in physical fitness, coat quality, and kidney function in older subjects treated with FOXO4-targeted constructs, reflecting an extension of health span rather than simply adding time to lifespan.
Persistent senescent cells contribute to many age-related problems, such as chronic inflammation, vascular damage, and tissue stiffness. Clearing them does not completely solve issues like stem cell exhaustion, but it may slow the rate at which regenerative capacity declines. By focusing on senescent cells, FOXO4-DRI offers a way to shift the balance from passive aging to active rejuvenation at the cellular level.
FOXO4-DRI Experimental Research
Insulin and Metabolic Regulation
FOXO family proteins sit downstream of insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors and act as key switches for metabolic gene programs. When FOXO signaling is altered, cells can lose proper control over glucose and lipid handling, leading to elevated blood sugar, increased circulating fats, and wider metabolic disruption. Such changes contribute to the vascular and organ damage commonly seen in metabolic disease. Modulating FOXO pathways offers a way to intervene closer to the core control system that determines how cells respond to insulin signals. FOXO4-DRI, by reshaping FOXO4 interactions, is being explored as a tool to adjust these downstream responses and potentially improve fasting glucose and lipid profiles in experimental models.
Cardiovascular Aging
With advancing age, the heart accumulates damaged and oxidized proteins that should normally be removed by proteasomes and autophagy systems. Declining activity of these clearance pathways correlates with increased stiffness, reduced contractile performance, and greater vulnerability to stress. FOXO proteins are important controllers of both proteasome function and cellular self-cleaning processes. Enhancing FOXO-driven housekeeping in cardiac tissue has been shown to lower the burden of damaged proteins. There is interest in whether a carefully tuned FOXO4-DRI-type approach could amplify these protective mechanisms in older hearts, supporting better maintenance of cardiac structure and function over time.
Neurodegeneration and Brain Health
Many neurodegenerative conditions, including common age-associated disorders, involve accumulation of misfolded or aggregated proteins and impaired cellular cleanup systems in the brain. Reduced proteasome and autophagy function has been documented across several such diseases. FOXO proteins are modified and regulated within the nervous system, where they influence stress responses, survival signaling, and protein turnover in neurons and glial cells. Experimental manipulation of FOXO activity is being investigated as a way to slow or counteract progressive loss of neural function. FOXO4-DRI and related constructs may help researchers test whether selectively adjusting FOXO4 pathways can support more efficient removal of toxic proteins and bolster neuronal resilience, potentially moderating the course of neurodegenerative processes.
Overall Perspective
FOXO4-DRI is best known for its ability to drive apoptosis in senescent cells, thereby improving tissue quality and healthspan in animal models. Beyond this, it serves as a valuable experimental tool for dissecting how FOXO4 participates in metabolic control, cardiovascular aging, and neurodegeneration. Ongoing studies aim to determine how broad its benefits may be and how to harness its senolytic properties safely and precisely.
In preclinical work, FOXO4-DRI has shown minimal reported side effects, limited impact when given orally, and strong uptake when delivered by subcutaneous routes in animals. Doses established in these models are specific to the experimental context and cannot be applied directly to people. At present, FOXO4-DRI is intended only for controlled scientific and educational research and is not approved for human use or unsupervised application.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.