Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
Glow Blend 70 mg
Total Glow Peptide Blend
This blend is available in two research configurations:
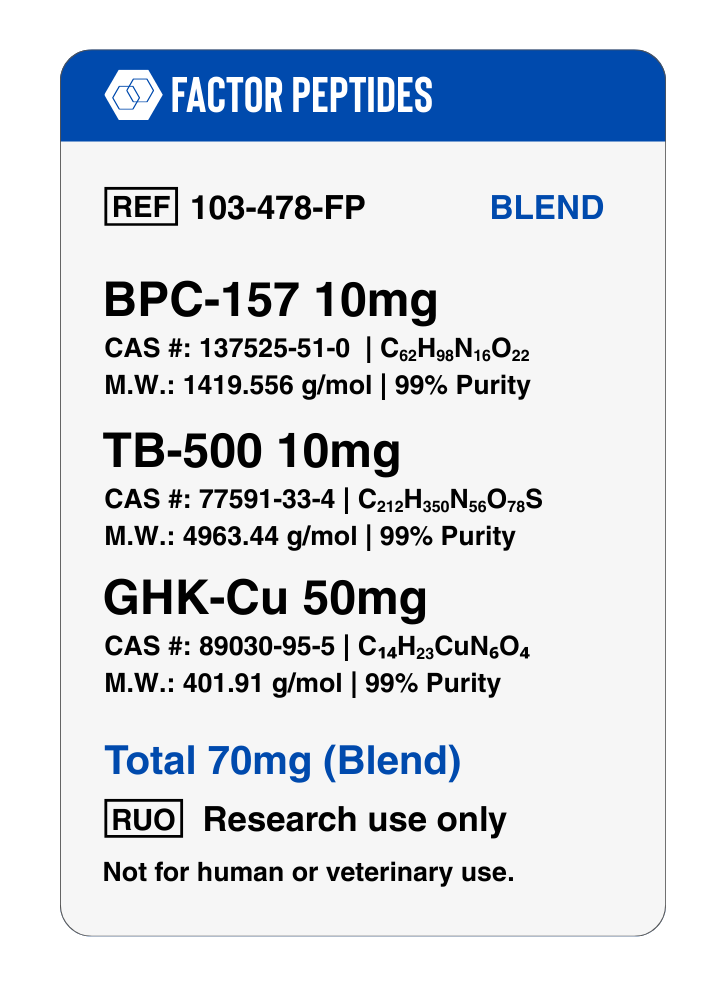
- BPC-157 5 mg, TB-500 5 mg, GHK-Cu 20 mg (30 mg total blend)
- BPC-157 10 mg, TB-500 10 mg, GHK-Cu 40 mg (60 mg total blend)
Individual Peptide Mechanisms
BPC-157
BPC-157 is a synthetic gastric pentadecapeptide that has been studied in preclinical models for its ability to support blood vessel formation, fibroblast movement, and surface layer repair. Experimental work suggests that it influences vascular and adhesion signaling pathways, as well as nitric oxide–related networks, contributing to observed support of tendon, muscle, and intestinal tissue in non-clinical research.
TB-500
TB-500 is a 43–amino acid research peptide related to an actin-binding protein fragment. It has been explored for its role in cell migration, formation of new microvessels, and modulation of inflammatory responses. Studies indicate that it can affect progenitor cell activity and support repair processes in cardiac, skin, and connective tissue models.
GHK-Cu
GHK-Cu is a copper-binding tripeptide that has been widely examined for its involvement in wound closure, collagen production, and hair follicle support in experimental systems. It appears to regulate gene networks linked to tissue remodeling and to influence antioxidant and anti-inflammatory defenses, in part through transforming growth factor and matrix-enzyme related pathways.
Synergy in Research Settings
When studied together, BPC-157, TB-500, and GHK-Cu provide a way to investigate multi-pathway support of tissue repair and inflammatory balance. The blend brings together several complementary mechanisms:
- Vascular support: BPC-157 and TB-500 have both been associated with growth factor–driven
vascular responses, while GHK-Cu has been linked to endothelial cell activity in laboratory models. - Cell movement and matrix organization: TB-500 is closely tied to actin dynamics and cell
motility, whereas BPC-157 and GHK-Cu have been studied for their effects on extracellular matrix production,
fibroblast behavior, and structural remodeling. - Inflammatory and oxidative balance: All three peptides have been examined for their
potential to temper oxidative stress and cytokine-driven inflammation, which may be relevant in research on
long-standing or complex tissue challenges.
Taken together, these overlapping and complementary mechanisms make the blend a useful tool for exploring tissue regeneration, structural remodeling, and inflammatory modulation in musculoskeletal, skin, and post-intervention research models. This material is intended strictly for laboratory use and is not designed for diagnostic or therapeutic application in humans or animals.
$110.00
All Products
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
BPC 157 + TB500 (Thymosin Beta 4) + GHK Cu Blend
BPC 157, TB500 (Thymosin Beta 4 fragment), and GHK Cu are each well studied investigational peptides with potent activity in tissue repair and inflammatory modulation in animal models. Individually, they have been shown to promote wound healing, support muscle and tendon recovery, influence gene expression, and counter certain age associated changes in preclinical studies.
The BPC 157 + TB500 + GHK Cu blend is formulated to simplify research on their combined actions. By providing all three peptides in a single preparation, the blend streamlines ordering, storage, dosing, and administration. This allows investigators to focus on experimental design and outcome measurement rather than managing multipleseparate vials and protocols.
Because each peptide acts through distinct yet overlapping pathways, co administration may produce synergistic effects on inflammation, angiogenesis, tissue remodeling, and cellular stress responses. The blend is therefore of interest for research on musculoskeletal injury, dermal repair, cardiovascular insult, and broaderinvestigations into healthspan and aging biology.
Component Peptides and Biochemistry
BPC 157
BPC 157 is a pentadecapeptide derived from the naturally occurring Body Protective Compound found in gastric juice. Animal research indicates broad protective and pro healing effects in the gastrointestinal tract, liver, pancreas, ligaments, tendons, muscle, cornea, heart, brain, and peripheral nerves.
Although its primary receptor has not been fully identified, several biochemical features are clear:
- Rapid distribution: Within approximately 10 minutes of administration in animal models,
BPC 157 is detectable throughout the body, with peak tissue levels at about 1 hour and a gradual decline over
roughly 48 hours. Highest levels are seen in kidney, liver, thymus, and spleen, with appreciable levels also
in lung, muscle, brain, and skin. - NO signaling: BPC 157 strongly influences nitric oxide (NO) pathways, including NOS
especially eNOS expression. It has been shown to counteract NO synthase inhibitors such as L NAME and is
associated with increased antioxidant enzyme expression including HO 1. - Gene expression: BPC 157 modulates expression of genes such as Egr, Nos,
Srf, Vegr, Plcγ, and Kras, which are involved in vascular adhesion,
thrombosis, and immune and inflammatory responses. Expression changes appear time dependent, suggesting a
finely tuned regulatory effect.
TB500 (Thymosin Beta 4 Fragment)
TB500 is a synthetic fragment of thymosin beta 4, a naturally occurring actin binding protein implicated in tissue repair and regeneration. TB500 shows activity in cardiac tissue, skeletal muscle, dermal and ocular repair, and immune modulation in preclinical models.
TB500 exerts its effects through two main mechanisms:
- Actin regulation: TB500 binds and sequesters G actin, influencing cell motility, shape,
division, and migration. This contributes to enhanced wound closure, immune cell trafficking, and blood
vessel formation. - Gene and pathway modulation: TB500 impacts NO synthesis, angiogenesis, cell proliferation,
and inflammatory signaling. It helps regulate NF κB and Toll like receptor pathways and suppresses the release
of pro inflammatory cytokines such as TNF α and IL 1 receptor associated kinases. It activates PI3K Akt eNOS,
Notch, and Ang1 Tie2 pathways for tissue repair and modulates TGF β and Wnt pathways to reduce fibrosis and
potentially support hair follicle activity.
GHK Cu
GHK Cu is a naturally occurring copper tripeptide complex (glycyl histidyl lysine bound to Cu II) identified in plasma, saliva, and urine. It is widely studied for its role in wound healing, collagen synthesis, fibroblast growth, and cosmetic skin applications.
Key biochemical properties include:
- Matrix remodeling: GHK Cu stimulates matrix metalloproteinases to remodel damaged proteins
while upregulating anti proteases that protect healthy matrix components. This balanced activity supports
dermal repair and improved skin architecture. - Antioxidant and anti inflammatory actions: GHK Cu upregulates antioxidant systems (for
example superoxide dismutase and glutathione related pathways) and downregulates inflammatory mediators such
as TNF α and IL 6 in animal models. - Gene expression: GHK Cu has been reported to influence a large set of human genes related to
tissue remodeling, stress response, and cellular repair, positioning it as a broad regulator of regenerative
processes.
Blend Research and Potential Synergy
1. Anti Inflammatory Pathways
All three peptides exhibit anti inflammatory activity in preclinical studies but act through distinct nodes in the inflammatory network:
- BPC 157 modulates NO signaling and eNOS expression, helping to normalize vascular tone,
cytokine release, and immune cell behavior. It has markedly reduced inflammation in models of gastrointestinal
ulceration and interstitial cystitis. - TB500 downregulates master inflammatory mediators including NF κB and key cytokines such as
TNF α and IL 6, while engaging pathways that promote resolution and repair. - GHK Cu scavenges free radicals, buffers NO related oxidative damage, and also suppresses
TNF α and IL 6. This may complement TB500’s cytokine modulation while protecting tissues from excess ROS
generated during inflammation and repair.
When used together, BPC 157 and TB500 can address inflammation via NO homeostasis and cytokine control, while GHK Cu provides oxidative protection and additional cytokine modulation. This multi node coverage may allow for more precise tuning of the inflammatory response in animal models with lower individual doses.
2. Tissue Repair and Regeneration
BPC 157, TB500, and GHK Cu have independently shown strong pro healing profiles in multiple tissues in animal studies. Their combined use is of interest where accelerated, high quality repair is desired.
- BPC 157 supports all phases of wound healing, improving structural coherence and functional
outcomes. It increases growth hormone receptor expression on fibroblasts at injury sites, allowing localized
amplification of GH signaling without systemic GH elevation. - TB500 enhances collagen deposition and extracellular matrix formation by fibroblasts and
activates satellite cells and other progenitor populations that differentiate into repair specific cell types.
It has demonstrated benefits in tendon, muscle, cardiac, dermal, and ocular repair in preclinical models. - GHK Cu reduces free radical burden and supports matrix remodeling during accelerated healing,
which may limit excessive scarring and preserve tissue quality. It is known for promoting smoother, more
organized dermal repair.
In combination, BPC 157 can recruit and sensitize repair cells, TB500 can drive structural rebuilding and progenitor activation, and GHK Cu can protect the microenvironment from oxidative damage and disordered remodeling. This triad may be especially valuable in models of tendon and ligament injury, surgical wounds, and chronic ulcers.
3. Antimicrobial and Barrier Support
Infection control is a major determinant of wound outcomes. The component peptides contribute in complementary ways:
- TB500 exhibits direct antimicrobial activity and improves penetration of endogenous and
exogenous antimicrobials into tissue. - GHK Cu can combine with fatty acids from damaged tissue to form antimicrobial complexes that
reduce bacterial and fungal colonization, with reported reductions in wound infection rates in animal models. - BPC 157 augments blood flow and immune cell recruitment to injured regions, indirectly
supporting host defense and clearance of debris.
Together, these effects may create a more hostile environment for pathogens while preserving and restoring tissue integrity in research models.
4. Anti Aging and Healthspan Related Effects
The blend has attracted interest for its potential to impact multiple hallmarks of aging in animal studies:
- TB500 supports regeneration in tissues with limited intrinsic repair capacity, such as
myocardium and skeletal muscle. It has been shown to improve cardiomyocyte survival, activate epicardial
progenitors, and enhance cardiac function after coronary ligation. It also reduces excessive inflammatory
damage in systemic conditions like sepsis. - BPC 157 has been reported to protect cardiac tissue against necrosis, improve blood flow,
reduce thrombosis risk, and support repair after cardiovascular insult in animal models. Similar protective
effects have been noted in the CNS, GI tract, kidney, bladder, and musculoskeletal tissues. - GHK Cu modulates a broad gene network associated with inflammation, matrix turnover, DNA
repair, proteasome function, and antioxidant defense. It has reduced oxidative stress, downregulated NF κB,
and influenced epigenetic pathways linked to neurodegeneration and cognitive decline in preclinical studies.
Collectively, these peptides touch multiple layers of the aging process including chronic inflammation, impaired regeneration, oxidative stress, and matrix degeneration. The blend provides a tool to explore whether coordinated modulation of these pathways can extend healthspan in experimental systems by improving both damage resistance and repair quality.
BPC 157 + TB500 (Thymosin Beta 4) + GHK Cu Blend Summary
The BPC 157 + TB500 + GHK Cu blend combines three well known research peptides with complementary actions in inflammation control, tissue repair, vascular support, and oxidative balance. While each peptide has been studied extensively on its own in animal and cell models, their combined use offers a way to investigate potential synergy across multiple repair and longevity related pathways.
This blend is particularly suited for:
- Preclinical models of musculoskeletal and tendon injury
- Dermal and surgical wound repair studies
- Cardiac and vascular insult models
- Exploratory research on aging mechanisms and healthspan
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
All articles and product information provided on this website are for informational and educational purposes only.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in vitro studies only. In vitro studies Latin “in glass” are performed outside of living organisms. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment, or disease. Any form of bodily introduction into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law.
BPC 157 + TB500 + GHK Cu Blend for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only purchase this blend if you are a properly licensed and qualified researcher.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.