Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
Ipamorelin
Ipamorelin is a highly selective growth hormone secretagogue that binds specifically to the ghrelin/GH secretagogue receptor. As one of the most targeted GH-releasing peptides, it has demonstrated the ability to stimulate GH release without influencing levels of ACTH, prolactin, FSH, LH, TSH, or cortisol.
Its remarkable selectivity makes ipamorelin a valuable subject in research not only for its potential therapeutic effects but also for its role in advancing understanding of receptor-specific binding mechanisms. In experimental models, ipamorelin plays a key role in promoting the growth and repair of musculoskeletal tissues, making it an area of interest in regenerative and performance-related studies.
Price range: $40.00 through $65.00
Cellular Age Support Peptides
Cellular Growth Research Peptides
Metabolic Activation Peptides
Metabolic Research Peptides
Popular Peptides
Reproductive System Research Peptides
Tissue Integrity Research Peptides
Uncategorized
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
What Is Ipamorelin?
Ipamorelin is a short peptide capable of binding to the ghrelin and growth hormone secretagogue receptor. It is one of the most selective growth hormone (GH) secretagogues identified to date and, in laboratory studies, has shown no measurable effect on ACTH, prolactin, follicle stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, or cortisol release.
Because of its selectivity, ipamorelin has attracted interest both as a potential therapeutic and as a model peptide for studying how receptor binding specificity can be achieved in peptide design.
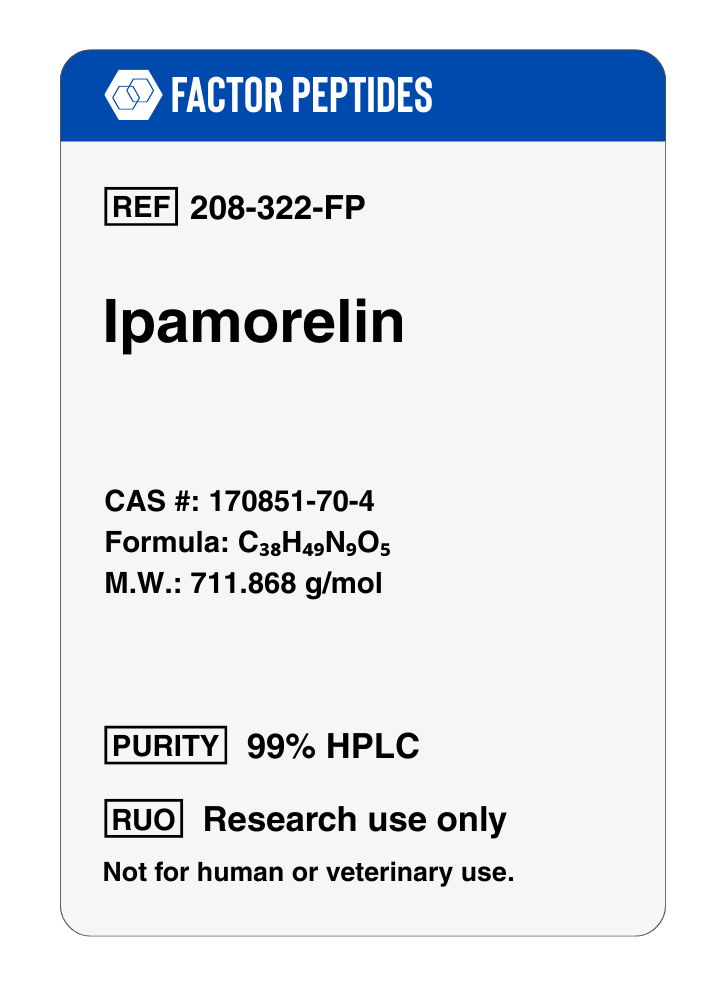
Ipamorelin Structure
Ipamorelin Peptide Structure
Source: PubChem
- Peptide Sequence: Aib His D 2Nal D Phe Lys
- Molecular Formula: C38H49N9O5
- Molecular Weight: 711.868 g/mol
- PubChem CID: 9831659
- CAS Number: 170851 70 4
Ipamorelin Research
1. Ipamorelin and Negative Corticosteroid Effects
Glucocorticoids, widely used to treat inflammation in conditions ranging from cancer to autoimmune disease, are associated with serious side effects that often limit their use. Mitigating these adverse effects could allow higher dosing and longer treatment durations, improving overall outcomes.
In several studies, ipamorelin has been shown to reduce or even reverse a number of glucocorticoid induced side effects, highlighting its potential as a supportive agent in long term steroid therapy.
2. Ipamorelin and Bone Health
One of the most significant complications of prolonged glucocorticoid use is bone density loss and increased fracture risk. Existing therapies for steroid induced osteoporosis, such as bisphosphonates, hormone therapies, and monoclonal antibodies, can be effective but are limited by side effects, cost, or incomplete efficacy.
In rat models, ipamorelin has been shown to completely prevent bone loss due to corticosteroid exposure and to produce approximately a four fold increase in bone formation compared to untreated controls. Additional studies indicate that ipamorelin also increases bone mineral density systemically, thereby strengthening both existing bone and newly formed bone.
At the same time, ipamorelin appears to offset other steroid related side effects, including muscle wasting and increased visceral fat deposition.
3. Ipamorelin and Muscle Growth
Growth hormone and GH secretagogues such as ipamorelin have been investigated for their ability to counter the catabolic, muscle wasting effects of glucocorticoids. In rat models receiving glucocorticoids, ipamorelin administration reduces nitrogen wasting in the liver and improves overall nitrogen balance.
Muscle wasting is a common, treatment limiting adverse effect of long term steroid use. The capacity of ipamorelin to help preserve muscle mass while also supporting bone density makes it a candidate for integrated approaches to glucocorticoid toxicity management.
4. Ipamorelin and Diabetes
Research in diabetic rats suggests that ipamorelin can potentiate insulin release. The mechanism appears to involve indirect stimulation of calcium channels on pancreatic islet cells, where insulin is synthesized and stored.
By illuminating how ipamorelin modulates pancreatic function, these studies may provide insights into functional limitations in type 2 diabetes and inform the development of novel therapeutics or preventative strategies.
5. Studied for Treatment of Post Operative Ileus
Post operative ileus (POI) is a common complication after surgery, especially abdominal procedures. It is characterized by delayed gastrointestinal motility and an inability to tolerate oral nutrition, which prolongs hospital stay and recovery time.
Ipamorelin has been tested in multiple proof of concept clinical trials as a potential treatment for POI. Data suggest that ipamorelin administration can shorten time to first meal by approximately 12 hours.
Despite this early signal of efficacy, development in this indication was discontinued when the sponsoring company concluded that the observed benefit was insufficient to support a commercial product. There remains interest in exploring whether optimized dosing, alternative formulations, or combination therapies could enhance the clinical impact of ipamorelin in GI motility disorders.
In preclinical models of POI:
- The amount of radiolabeled food remaining in the stomach is reduced in rats with POI after ipamorelin treatment, even relative to rats without POI.
- The geometric distribution of food along the GI tract in ipamorelin treated POI rats resembles that of non-POI controls.
- Food is located more distally in the GI tract following ipamorelin administration, indicating improved motility.
6. Ipamorelin as a Ghrelin Receptor Probe
Ipamorelin is a highly selective ghrelin receptor agonist with strong binding to the ghrelin receptor. Ghrelin receptor expression is known to increase in certain cancers (such as human carcinomas) and in heart failure.
Based on these features, researchers have proposed using ipamorelin as a positron emission tomography (PET) probe to visualize ghrelin receptor distribution in vivo. In vitro studies confirm that ipamorelin can serve as a feasible scaffold for PET probe development and highlight its synthetic accessibility.
Ongoing work is focused on assessing in vivo probe performance and establishing standards for interpreting PET images generated using ipamorelin based tracers.
Ipamorelin Is Neglected in Research
Although ipamorelin does not currently have orphan drug status, it is relatively neglected in contemporary research. Interest diminished after development for post operative ileus was discontinued, despite encouraging preclinical and early clinical data.
Ipamorelin remains a versatile tool compound with potential applications as a therapeutic candidate and as a probe for understanding key disease pathways. Renewed investigation may reveal additional benefits in glucocorticoid toxicity, metabolic disease, bone and muscle health, and diagnostic imaging.
Ipamorelin Summary and Research Use Only Disclaimer
Ipamorelin is a selective ghrelin and growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist with demonstrated activity in preclinical models of bone loss, muscle wasting, glucocorticoid side effects, diabetes, gastrointestinal motility, and receptor targeted imaging. Its limited off target endocrine effects and high receptor selectivity make it a useful molecule for dissecting GH related pathways and for exploring new therapeutic strategies.
Ipamorelin exhibits moderate side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kilogram dosage in mice does not scale to humans.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
All articles and product information provided on this website are for informational and educational purposes only.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in vitro studies only. In vitro studies (Latin “in glass”) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment, or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
Ipamorelin for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy Ipamorelin if you are a licensed researcher.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.