Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
Pinealon
Pinealon is a short, three-amino-acid synthetic peptide that has demonstrated potential in protecting cells from hypoxic damage and modulating brain function. Research highlights its ability to influence circadian rhythms, support memory formation, and enhance learning capacity. Pinealon has also shown promise in mitigating age-related cognitive decline, particularly within the central nervous system. Its neuroprotective qualities make it a candidate for further exploration in the treatment of disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of cognitive impairment.
Price range: $60.00 through $75.00
All Products
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
What Is Pinealon?
Pinealon is a very short regulatory peptide built from three amino acids. It belongs to a group of synthetic compounds often called peptide bioregulators, which are investigated for their ability to influence how genes are switched on and off inside cells.
In experimental models, Pinealon has been associated with changes in behavior and with the protection of sensitive cell types, particularly nerve cells, under low-oxygen conditions. By acting on structures involved in timing and hormonal signaling, it is thought to help stabilize daily sleep–wake patterns, support more balanced processing of drugs and other substances, and contribute to healthier memory and learning functions.
Pinealon Structure
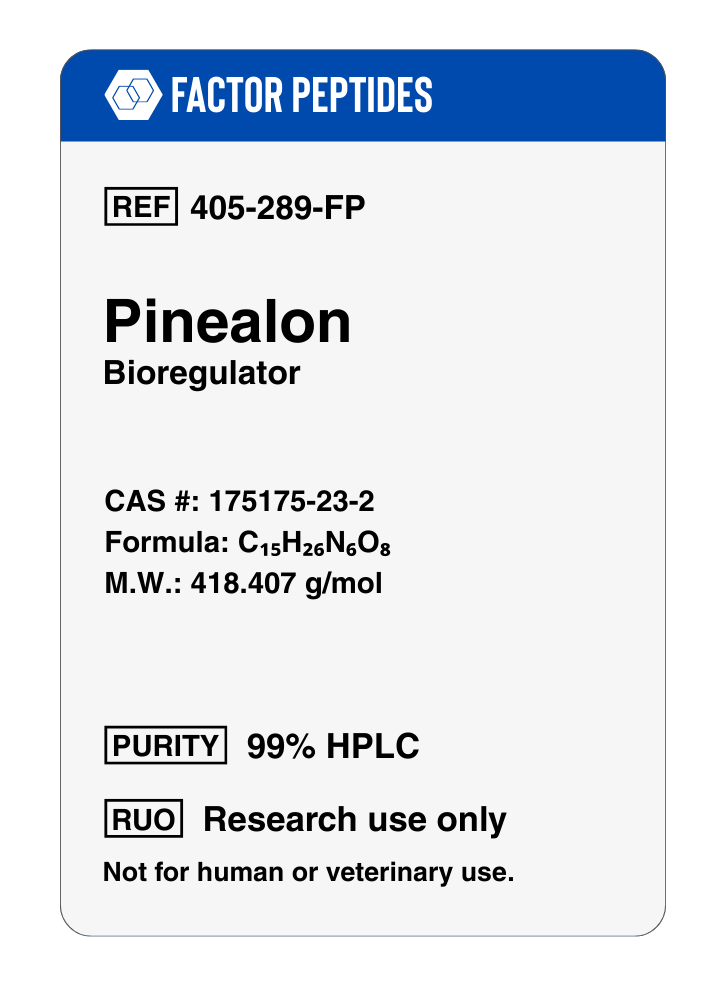
Sequence: Glu-Asp-Arg
Molecular Formula: C15H26N6O8
Molecular Weight: 418.407 g/mol
PubChem CID: 18220191
Synonyms: Glutamylaspartylarginine, T-33 peptide
Pinealon and Gene Regulation
Pinealon appears to act differently from many signaling peptides that rely on receptors at the cell surface or within the cytoplasm. Instead of working through these conventional docking sites, it seems to exert its influence inside the cell nucleus itself.
Laboratory studies using cultured cells suggest that Pinealon is small enough to pass directly through both the outer cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. Once inside the nucleus, it can associate with genetic material and influence which genes are actively being transcribed.
This direct interaction with DNA provides a plausible explanation for the wide range of cellular effects attributed to Pinealon, since altering patterns of gene expression can have downstream impacts on many different biological processes at once.
Pinealon Research
Pinealon and Aging
Experimental work suggests that Pinealon may help slow certain markers of biological aging, particularly in the central nervous system. In animal and cell models, the peptide has been associated with more favorable patterns of brain metabolism and function, leading to the suggestion that it may support a “younger” functional state in neural tissue.
Pinealon is not limited to the brain. Studies on muscle cells indicate that it can influence the expression of irisin, a messenger protein linked to protection of muscle fibers during exertion, enhanced fat use, and telomere support. Higher irisin activity has been associated with resistance to oxidative stress and with beneficial effects seen in calorie restriction. Because irisin also appears in other tissues, Pinealon’s influence on this pathway may contribute to broader, body-wide support of cellular longevity mechanisms.
Neuron Protection and Oxidative Stress
In prenatal and adult animal models, Pinealon has been shown to help nerve cells withstand low-oxygen conditions and oxidative stress. In these experiments, treatment was associated with lower accumulation of reactive oxygen species and fewer dying cells in vulnerable brain regions, which translated into better preservation of movement and cognitive performance.
Further work has shown that Pinealon modifies the cell cycle in response to stress, activating proliferative pathways that counterbalance damage signals. Rather than driving uncontrolled growth, this shift appears to help maintain viable cell numbers in environments where oxidative injury would otherwise lead to increased cell loss.
Pinealon also supports the brain’s own antioxidant defenses and can reduce overactivation of excitatory pathways, including those associated with NMDA-type receptors. Excessive stimulation of these receptors is known to contribute to neuron damage in situations such as withdrawal from certain substances, traumatic brain injury, and ischemic events.
Because Pinealon boosts irisin expression and irisin itself is now known to act in the brain, there is growing interest in a possible communication link between muscle and nervous system during physical activity. Irisin in the central nervous system has been tied to neuronal differentiation, energy management, and activation of genes in memory-related structures such as the hippocampus. By sustaining irisin levels, Pinealon may reinforce these adaptive responses.
Pinealon and Mood-Related Pathways
Cell culture studies using brain cortex tissue have found that Pinealon can enhance the expression of an enzyme critical for serotonin synthesis. This effect appears to be mediated by epigenetic mechanisms that adjust how accessible certain genes are, rather than by direct receptor binding.
Serotonin plays roles in mood, stress resilience, and neural protection. Many commonly used antidepressant medications act indirectly on serotonin signaling, but can be associated with significant side effects. The observation that Pinealon may increase serotonin production at the gene-expression level has led to interest in its potential as a more physiology-oriented way of influencing mood-related pathways in experimental systems.
Cell Survival, Caspase-3, and Tissue Protection
One of the key insights into Pinealon’s action came from models of reduced blood flow to the brain. In these studies, Pinealon lowered the activity of cell-signaling cascades that normally lead to increased production of caspase-3, a central executioner enzyme in programmed cell death.
By reducing caspase-3 activation, Pinealon helps cells resist apoptosis during and after oxygen deprivation. Similar protective patterns have been observed in heart muscle models after experimental heart attacks, where Pinealon treatment reduced caspase-3 levels and was associated with less structural damage and remodeling.
In skin tissue, Pinealon’s suppression of caspase-3 appears to favor cell renewal and regeneration. Both young and aged animals show enhanced cell proliferation in the skin after exposure, along with reduced age-related changes. These findings have prompted interest in Pinealon as part of broader approaches to wound care and skin health in research settings.
Sleep, Circadian Rhythm, and Systemic Effects
Pinealon’s name reflects its connection to the pineal gland, which governs daily biological rhythms and melatonin production. Experimental data indicate that Pinealon can help normalize disrupted circadian patterns, such as those caused by shift work, irregular schedules, or long-distance travel.
In models of rhythm disturbance, Pinealon appears to help reset pineal function toward a baseline pattern, with downstream improvements reported in sleep quality, blood pressure regulation, mood, and overall daytime functioning. Because sleep disruption is tightly linked to accelerated aging, cardiovascular strain, impaired healing, and cognitive decline, the ability to stabilize circadian signaling may be one of the most consequential aspects of Pinealon’s research profile.
Experimental Status
Across animal and cell-based studies, Pinealon has generally shown a favorable tolerance profile, with good uptake when delivered by injection and limited oral absorption. The doses used in these models are tailored to the species and experimental design and cannot be directly translated to people.
Pinealon remains an investigational peptide bioregulator. Its potential roles in aging, neuroprotection, mood regulation, tissue repair, and sleep stabilization are still being mapped out, and current evidence comes largely from preclinical research rather than established clinical use.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.