Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
Selank
Selank is a synthetic peptide modeled after tuftsin, a naturally occurring immunomodulatory peptide. It is primarily known for its anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects, but research also supports its role in enhancing cognitive functions such as memory and learning. Additionally, Selank has demonstrated potential in modulating pain perception, suggesting broader applications in neurological and psychological research.
Price range: $40.00 through $65.00
All Products
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
Selank Overview
Selank is a laboratory-designed peptide that has been studied for its potential to support cognition and to ease anxious states. It is based on a naturally occurring immune-signaling fragment found in the body, but its sequence has been extended to improve stability and persistence in circulation.
Experimental work suggests that Selank can influence several systems at once, including inflammatory messengers, specific immune cell populations, mood-related brain chemicals, and growth factors that support the survival and plasticity of neurons. Through these combined actions, it has attracted interest as a candidate for regulating stress responses and mental clarity.
Selank has been examined in human studies as a possible option for people experiencing chronic, excessive anxiety and related symptoms, with a focus on its calming effects without strong sedation. Research is ongoing to clarify its full range of activity and long-term impact.
Selank Structure
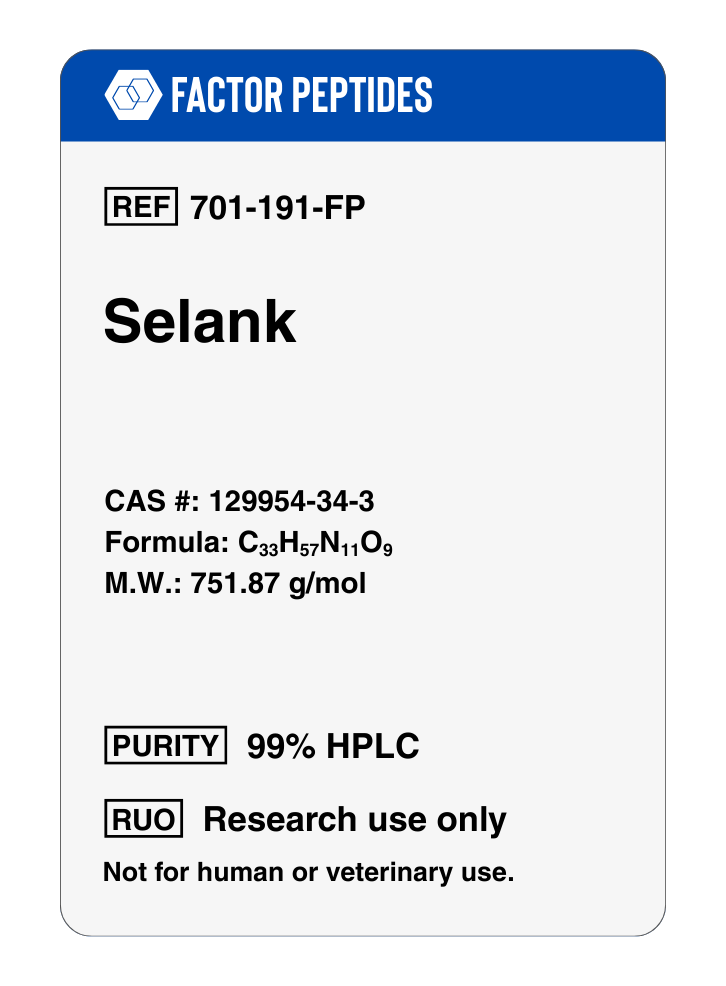
Sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg-Pro-Gly-Pro
Molecular Formula: C33H57N11O9
Molecular Weight: 751.87 g/mol
CAS Number: 129954-34-3
Synonyms: Selanc
Selank Research
Influence on Anxiety and GABA Signaling
Experimental and clinical work suggests that Selank can ease anxious states while also protecting brain cells. Its overall calming effect has often been compared with that of traditional anti-anxiety medications that act through GABA receptors. Reported outcomes include reduced tension, better mood, lower perceived stress, and a gentler settling of the nervous system. At modest amounts, Selank may also promote a mild sense of relaxation.
Unlike many classic anti-anxiety drugs, Selank has not been associated in research settings with drug-seeking behavior, withdrawal symptoms, or memory blackouts. This distinction has made it a peptide of interest for scientists exploring alternatives to conventional tranquilizers.
Gene-level studies in animals show that Selank alters the activity of dozens of genes involved in GABA-related signaling. A sizable subset of GABA-linked genes appears to shift their expression when the peptide is present. Current models propose that Selank does not simply flood the brain with more GABA, but instead changes how sensitive GABA receptors are to the body’s own calming signal, which may also explain why it can work alongside other GABA-acting compounds.
Enkephalins and Stress Response
Some of Selank’s actions may be tied to its influence on enzymes that break down enkephalins. Enkephalins are short peptides the body produces to dampen pain and modulate the stress response. In people with chronic anxiety and phobic tendencies, experiments have shown that the enzymes responsible for degrading enkephalins can be more active than usual, shortening the lifespan of these natural comfort molecules.
Laboratory data indicate that Selank can slow this breakdown by inhibiting enkephalin-degrading enzymes. In animal models that are predisposed to anxious behavior, preserving enkephalins in this way appears to contribute to a calmer, more resilient stress response.
Immune Regulation in Anxiety States
Selank has also been studied as an immune modulator. In groups with mood and anxiety symptoms, the peptide has been observed to influence the activity of genes that code for inflammatory messengers, including certain cytokines. In particular, it can reduce the expression of a key pro-inflammatory signal in individuals with mood disturbance, while leaving this pathway largely unchanged in healthy volunteers.
Comparisons with standard anti-anxiety options show that while both approaches can reduce worry and inner tension, Selank appears to exert additional effects on fatigue, pain, and other “drained” or asthenic sensations that accompany some anxiety syndromes. This broader impact may reflect its role in fine-tuning inflammatory cascades as well as its interaction with endogenous pain-relieving peptides.
Animal studies of the spleen and other immune tissues reveal that Selank can temporarily shift expression of several genes involved in immune development, chemokine signaling, and receptor balance. These findings support the view that the peptide is capable of subtly reorienting immune responses rather than bluntly suppressing them.
Memory, Learning, and Cognitive Effects
High levels of anxiety are well known to interfere with attention, learning, and recall. While easing anxiety can itself improve performance, Selank appears to have additional, more direct effects on memory processes.
In behavioral experiments, animals trained on reward-based tasks recalled learned patterns more consistently when given Selank compared with controls. Memory traces remained more stable over time, suggesting that the peptide supports the consolidation phase in which short-term information is stored more permanently. Notably, these improvements were observed even when anxiety was not the main limiting factor.
Molecular analysis in brain regions involved in learning, such as the hippocampus, shows that Selank alters the expression of numerous genes related to membrane structure and ion transport. Because these features shape how neurons fire and communicate, such changes may help explain the observed benefits in learning and memory. Additional studies indicate that Selank can partially restore cognitive performance after certain types of chemically induced brain injury, hinting at a possible protective role in the face of neural stress.
Selank and Pain Perception
Beyond its emotional effects, Selank may also influence how the body processes discomfort. By slowing the breakdown of enkephalins, it effectively supports the body’s own opioid-like system, which helps soften pain signals and modulate the stress response. This dual action on both emotional tension and physical perception may be especially relevant in conditions where anxiety, fatigue, and chronic aches coexist.
Research Use Only
In experimental models, Selank has generally shown a low incidence of reported side effects and favorable absorption when administered by injection in animals, while oral use has appeared limited. Dosing used in animal work cannot be directly converted to human amounts. Selank is supplied for controlled scientific or educational research and is not intended for self-administration, medical treatment, or other human use.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.