Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
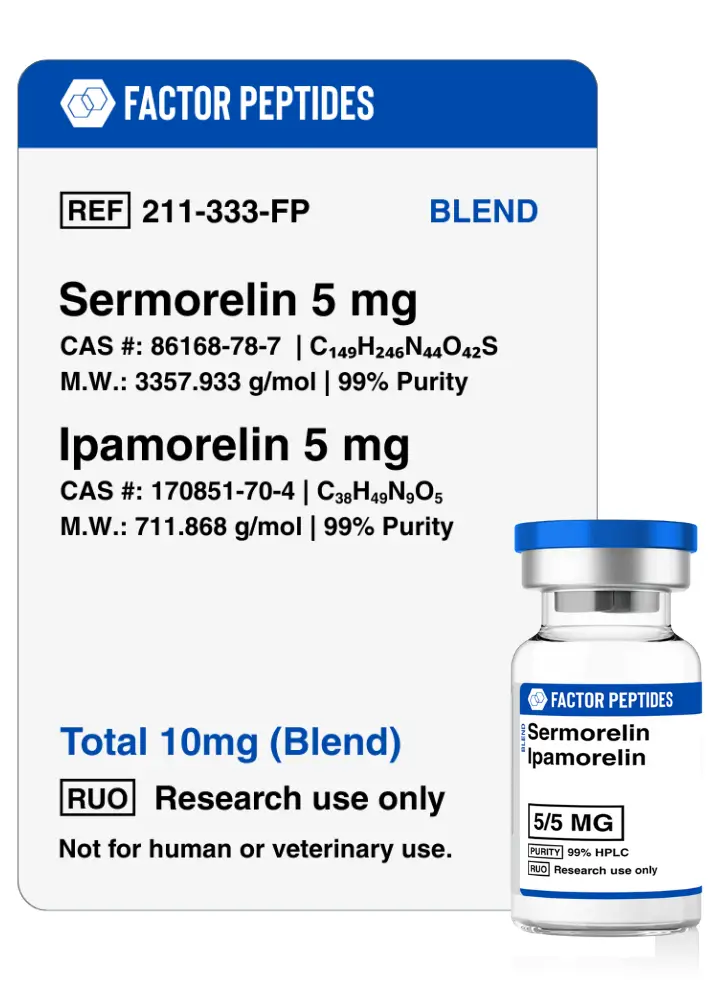
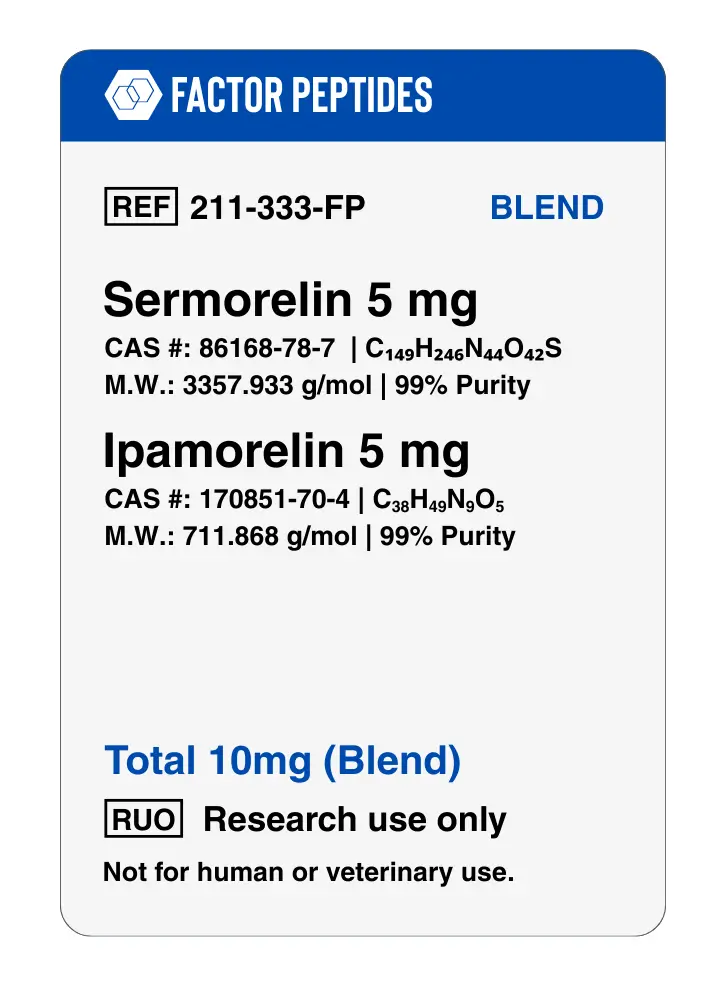
Sermorelin + Ipamorelin Blend
This 10mg blend pairs Sermorelin (5mg) with Ipamorelin (5mg), two peptides that work synergistically to significantly boost the body’s natural growth hormone release. Sermorelin acts as a GHRH analogue, stimulating the pituitary gland, while Ipamorelin is a selective growth hormone secretagogue that enhances this signal without elevating cortisol or prolactin levels. Together, they are researched for their potential to accelerate muscle growth, improve recovery, enhance tissue repair, promote better sleep, and deliver anti-aging benefits by amplifying growth hormone activity naturally.
$95.00
All Products
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
Sermorelin and Ipamorelin
Sermorelin and ipamorelin are often studied together as a way to stimulate the growth hormone (GH) axis through two complementary pathways. Sermorelin is a growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) analogue designed to preserve many of the beneficial properties of endogenous GHRH while limiting some of its drawbacks. Ipamorelin is a highly selective growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) agonist and a targeted analogue of ghrelin.
In experimental models, combining a GHRH analogue such as sermorelin with a GHSR agonist such as ipamorelin has been associated with synergistic increases in GH release. By acting at different regulatory points in the GH axis, this combination has been investigated for its potential to enhance GH-related effects on skeletal muscle, brain function, cardiovascular remodeling, and overall metabolic profile.
Cardiovascular Effects
Sermorelin has been examined in preclinical heart models for its impact on cardiac structure and function following injury. In pig models of myocardial infarction, GHRH analogues such as sermorelin have been associated with:
- Reduced cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) death
- Improved healing and structural remodeling after cardiac injury
- Increased growth of collateral blood vessels in affected regions
- Lower expression of markers linked to damaging inflammation
These tissue-level findings have correlated with changes in scar burden and improvements in certain measures of cardiac performance in these models.
In parallel, a form of the ghrelin receptor has been identified in cardiac tissue, where it appears to influence cardiac output and electrophysiologic stability. Administration of ghrelin and ghrelin analogues in animal models has been reported to reduce the risk of arrhythmias and to support recovery after cardiac injury. Together, these findings support ongoing interest in the sermorelin–ipamorelin combination as a research tool in cardiovascular physiology.
Central Nervous System and Sleep
Beyond its somatic effects, sermorelin has been explored for its potential impact on the central nervous system. In animal studies, GHRH analogues have been linked to changes in brain regions involved in cognition and to modulation of sleep–wake regulatory mechanisms.
Experimental work in non-human models suggests that an intact GHRH axis contributes to normal sleep architecture and that exogenous GHRH agonists may influence sleep quality and associated neuroendocrine rhythms. These observations have prompted further investigation into how sermorelin, alone or combined with ipamorelin, might be used as a probe of sleep regulation, neuroplasticity, and GH-dependent brain processes in controlled research settings.
Additional Experimental Findings for Ipamorelin
Ipamorelin has been studied as a selective GHSR agonist with GH-releasing properties and comparatively limited off-target activity. In various animal models, ipamorelin has been associated with:
- Support of bone turnover and bone mineral parameters
- Modulation of insulin dynamics in models of disordered glucose control
- Effects on gastrointestinal motility, particularly in the postoperative setting
These observations suggest that ipamorelin, especially when paired with a GHRH analogue like sermorelin, may be a useful tool compound for investigating GH- and ghrelin-related pathways in bone biology, metabolic regulation, and gut function.
Sermorelin and ipamorelin are supplied for educational and scientific research use only. They are not approved for self-administration, anti-aging programs, performance enhancement, or any therapeutic application outside of properly regulated studies. In animal work, both compounds have shown favorable subcutaneous bioavailability; however, dose-response relationships observed in non-human species do not translate directly to humans. Only qualified, licensed researchers should handle and use these peptides in appropriate laboratory or preclinical environments.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.