Product Usage: This product is intended solely for use as a research chemical. It is designated exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory testing. All information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. It is strictly prohibited to administer this product to humans or animals. Only licensed and qualified professionals should handle it. This product is not classified as a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misrepresented or used as such. This product is for research use only. Not for human consumption.
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4)
TB-500, also known as Thymosin Beta-4, is a short peptide made up of 43 amino acids and has been widely studied in experimental models for its impact on tissue health. Research indicates that it can support the formation of new blood vessels, guide the wound-repair process, help limit inflammation, and lessen oxidative stress in organs such as the heart and components of the central nervous system. Because it appears to play an important part in protecting tissues, aiding repair, and encouraging regeneration and structural remodeling after injury, it has become a subject of interest in areas related to longevity and age-related decline.
Price range: $40.00 through $65.00
All Products
- DESCRIPTION
- STORAGE
What Is TB-500?
TB-500 is a 43–amino acid synthetic analogue of thymosin beta-4 (TB-4), a peptide found naturally in nearly all mammalian cells. TB-500 is best known for its effects on actin dynamics, cell migration, and tissue repair. In animal models and in vitro studies, TB-500 has been observed to support new blood vessel growth, accelerate wound healing, decrease inflammation, and promote extracellular matrix production. Current research is investigating its potential to help reduce oxidative stress after spinal cord injury, support recovery following heart attack, and explore possible anti-aging–related applications in preclinical settings.
TB-500 Mechanism of Action
TB-500 represents the active region of TB-4, which functions primarily as an actin-binding protein. Actin is a critical structural protein in cells and a major component of microfilaments. These microfilaments help maintain cell shape, protect membrane integrity, support cell movement/migration, and participate in key steps of cell division. Actin is also an essential part of muscle fibers, and normal muscle contraction depends on its proper function. Actin-binding proteins such as TB-4 help sequester actin monomers so they are protected from degradation and remain available for assembly into microfilaments when needed.
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) Peptide Sequence
Sequence: Ac-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro-Asp-Met-Ala-Glu-Ile-Glu-Lys-Phe-Asp-Lys-Ser-Lys-Leu-Lys-Lys-Thr-Glu-Thr-Gln-Glu-Lys-Asn-Pro-Leu-Pro-Ser-Lys-Glu-Thr-Ile-Glu-Gln-Glu-Lys-Gln-Ala-Gly-Glu-Ser
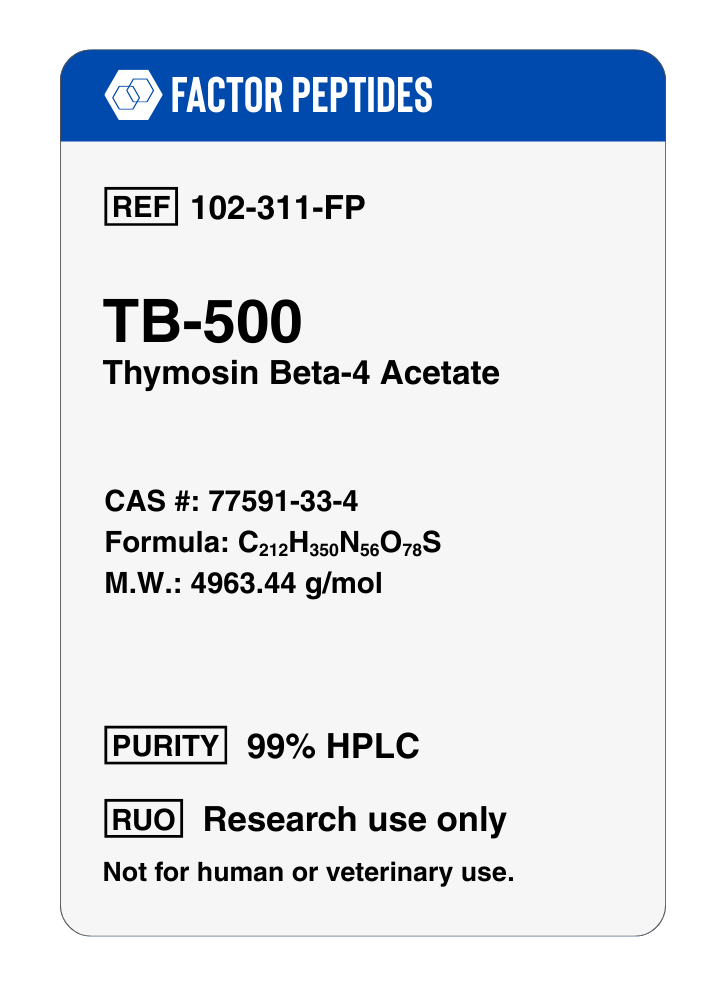
Molecular Formula: C212H350N56O78S
Molar Mass: 4963.4408 g/mol
CAS Number: 77591-33-4
PubChem: CID 16132341
TB-500 Research
1. TB-500 and Neurologic Function
In rodent models, TB-500 has been reported to support repair and remodeling in both central and peripheral nervous system tissues after injury. Although the precise mechanisms remain under investigation, studies suggest that TB-500 helps activate glial support cells, including oligodendrocytes, which play a key role in maintaining neuronal health. Increased activity of these support cells has been associated with enhanced blood vessel growth and improved neuron survival in damaged brain regions, along with measurable improvements in behavior, motor control, and cognitive performance in animal studies.
Recent work also indicates that TB-500 can help reduce oxidative stress following experimental spinal cord injury and may improve the survival of transplanted neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs). By improving the microenvironment for these cells, TB-500 and other TB-4–derived peptides are being explored as tools to better understand and potentially enhance spinal cord regeneration in preclinical models.
2. TB-500 and Blood Vessel Growth
TB-500 and TB-4 have been shown to stimulate expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a key signaling molecule involved in the growth of capillaries and small blood vessels. These processes are fundamental to wound repair, tissue remodeling, and even hair growth. Researchers believe TB-500’s role goes beyond VEGF regulation alone, and may extend to multiple steps in blood vessel formation, including extracellular matrix remodeling, vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and the differentiation of mesenchymal precursors toward endothelial cell lineages.
Loss-of-function models in which TB-4 is deficient show impaired blood vessel formation and stability, while exogenous administration of TB-4 or its active fragments improves capillary formation and pericyte recruitment after injury. These findings position TB-500 as a useful research tool for studying how blood vessels form and stabilize in response to tissue damage.
3. TB-500 and Hair Growth
The link between TB-500/TB-4 and hair growth was first noticed serendipitously. In mouse models engineered to be deficient in TB-4, shaved areas of fur regrew noticeably more slowly than in wild-type mice. Conversely, in mice genetically modified to express elevated levels of TB-4, shaved fur regrew faster than normal. Microscopic analysis in these models has shown increased numbers of hair shafts and more densely grouped hair follicles, suggesting a role for TB-4–derived peptides in hair follicle cycling and regeneration.
4. TB-500 and Antibiotic Synergy
The rise of multi-drug–resistant infections has highlighted the need for strategies that can improve the effectiveness of existing antibiotics. In one preclinical study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa eye infection in mice, a TB-4–based approach was evaluated as an adjuvant to ciprofloxacin, a commonly used antibiotic for this organism. In that model, the combination of TB-4 with ciprofloxacin improved healing, reduced inflammation, and promoted faster clinical recovery compared to antibiotic alone.
After five days of combined treatment, animals receiving both agents showed lower bacterial colony-forming units (CFUs), decreased neutrophil infiltration, and reduced levels of inflammatory reactive oxygen species. These results suggest that TB-500 and related peptides may help scientists explore new strategies for enhancing the activity of established antimicrobial therapies.
5. TB-500 and Cardiovascular Health
Over the past two decades, TB-4 and its derivatives have been examined in models of cardiovascular and renal disease. Although the underlying mechanisms are not fully defined, several recurring themes have emerged. First, TB-500 appears to promote the development of collateral blood vessels, which can help bypass obstructed arteries and improve tissue perfusion. Second, TB-500 has been associated with enhanced endothelial cell migration and improved survival of cardiac myocytes following ischemic events such as experimental heart attack. Third, TB-500 may act in combination with other signaling molecules to reduce inflammation and limit fibrosis, potentially improving structural and functional recovery after injury.
More recent work with biomaterial scaffolds and hydrogels incorporating collagen and TB-4 has shown that these systems can promote angiogenesis and epicardial cell migration in preclinical models, supporting interest in TB-500 as a tool to investigate heart repair and post-ischemic remodeling.
6. TB-500 and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and prion-related conditions remain challenging to treat. In experimental systems, TB-4 has been reported to enhance autophagy, the cellular “self-cleaning” process that helps remove misfolded proteins and damaged organelles. Autophagy is considered a key component of the central nervous system’s defense against protein-aggregation disorders. By boosting autophagic activity in preclinical models, TB-4–derived peptides like TB-500 are being studied as tools for probing how enhanced cellular clearance pathways might influence neurodegenerative disease progression.
7. TB-500 Has Wide Application
Because of its fundamental role in actin dynamics and cell structure, TB-500 has potential impact on multiple tissues and organ systems. This broad relevance has led to a diverse array of preclinical research efforts, ranging from heart and nervous system injury models to studies of wound repair, hair growth, and antibiotic synergy. TB-500 is therefore considered a high-interest research peptide and is likely to remain an active focus of investigation as scientists continue to explore its mechanisms and applications.
TB-500 exhibits minimal side effects in animal studies, with low oral and strong subcutaneous bioavailability reported in mice. Dose levels established in rodents do not directly translate to humans. TB-500 for sale at Peptide Sciences is supplied strictly for educational and scientific research and is not intended for human consumption or clinical use. Only qualified, licensed researchers should purchase TB-500.
Factor Peptides Storage Guidelines:
These peptides arrive in a dried, stabilized form produced by a process called lyophilization, or freeze drying. In this state, they are generally suitable for transport and short-term storage at typical room temperatures for several months.
Once the dry powder is mixed with bacteriostatic water and turned into a liquid solution, the storage requirements change. The reconstituted solution should be kept in a refrigerator to help maintain its properties, and is usually considered suitable for use for about 30 days under chilled conditions.
Lyophilization involves freezing the material and then exposing it to low pressure so that ice in the sample passes directly from solid to vapor, rather than melting. This leaves behind a light, porous, white solid that is more stable than the original liquid. In this form, the product can often be kept at room temperature until it is time to add diluent.
After delivery, it is good practice to protect the vials from heat and strong light. If the product will be used in the near future, storing the lyophilized powder or reconstituted solution in a refrigerator at temperatures below about 4°C (39°F) is typically appropriate. The dry form often remains intact at room temperature for a number of weeks, so this may also be acceptable when immediate refrigeration is not available and the intended use is relatively soon.
For storage over longer periods, such as many months or years, much colder conditions are preferred. Placing the vials in a deep freezer, around -80°C (-112°F), is commonly used to help preserve the structure and activity of peptides for extended time frames.